Timurid Empire: Rise, Conquests, and Cultural Legacy in Central Asia
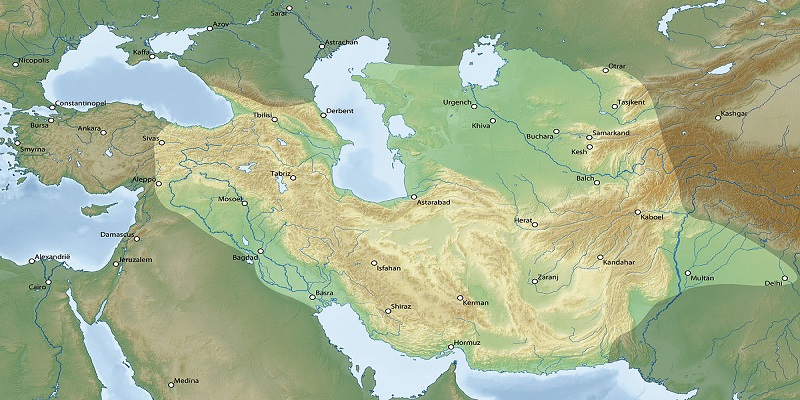
The Timurid Empire was a powerful state that emerged in Central Asia in the late 14th century. The empire was founded by Timur, a Turco-Mongol conqueror who had conquered vast territories across the region, including Persia, Mesopotamia, and parts of India. The Timurid Empire lasted from 1370 to 1507, and was known for its cultural and artistic achievements, as well as its military conquests.
Timur was born in 1336 in what is now Uzbekistan. He grew up in a region that was constantly being fought over by various tribal groups, and as a young man, he became a skilled warrior and leader. In 1360, Timur was captured by the ruler of Transoxiana, and spent several years as a prisoner. However, he eventually escaped and began building his own army.
By 1370, Timur had conquered much of Central Asia, including the cities of Samarkand and Bukhara. He then turned his attention to Persia, which was ruled by the Ilkhanate, a Mongol dynasty. In 1381, Timur defeated the Ilkhanate and established his own empire in Persia. Over the next few years, he conquered much of Mesopotamia and the Caucasus, and even launched a failed invasion of China.
Timur’s military campaigns were characterized by extreme brutality. He was known for his willingness to use terror tactics, such as massacring entire populations and building pyramids of skulls as a warning to his enemies. However, he was also a patron of the arts, and his capital city of Samarkand became a center of culture and learning.
After Timur’s death in 1405, his empire was divided among his descendants. However, the Timurid Empire continued to expand under the rule of Timur’s successors. In the early 15th century, the Timurids conquered much of northern India, including Delhi and the surrounding region. They also established a presence in the Middle East, with the conquest of Baghdad in 1401.
Despite their military successes, the Timurids were often beset by internal divisions and rivalries. This eventually led to the collapse of the empire in the late 15th century. By 1507, the Timurid Empire had been reduced to a small rump state in Central Asia, and was eventually conquered by the Uzbeks in 1510.
The legacy of the Timurid Empire is still felt today in Central Asia and the Middle East. The cultural and artistic achievements of the Timurids, such as the magnificent buildings and artworks of Samarkand, continue to inspire people around the world. However, the brutality and violence of Timur’s military campaigns also serve as a cautionary tale about the dangers of conquest and imperialism. Overall, the Timurid Empire was a complex and multifaceted entity, and its history is still being studied and debated by scholars today.