Legacy of the Lodhi Dynasty: Triumphs, Turmoil, and Timeless Contributions
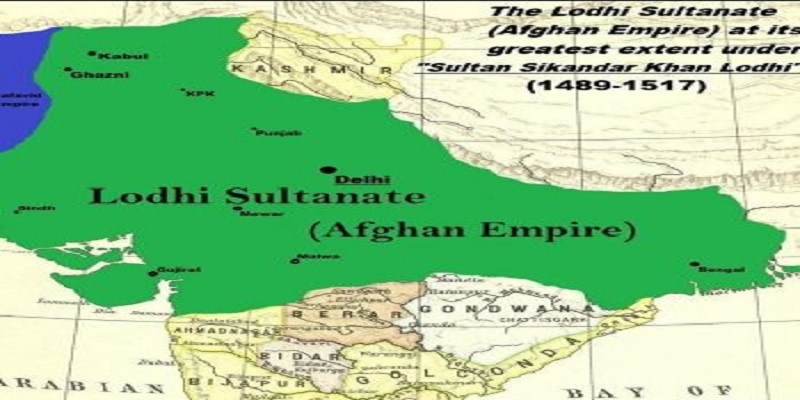
The Lodhi Dynasty was a powerful ruling dynasty that ruled over India from 1206 to 1526. It was founded by the Afghan ruler Bahlul Khan Lodi, who had established himself as the Sultan of Delhi after defeating the last of the Khilji rulers in 1296. The Lodhi Dynasty was the last of the Delhi Sultanate dynasties and was followed by the Mughal Empire.
The early years of the Lodhi Dynasty were marked by political instability and frequent power struggles between various factions within the royal court. However, under the leadership of Sikandar Lodi, the second ruler of the dynasty, the empire began to stabilize and prosper.
Sikandar Lodi was a capable ruler who made significant efforts to strengthen the administrative machinery of the empire. He reorganized the army and introduced several administrative reforms, including the appointment of a revenue officer for each district and the establishment of a centralized system for tax collection. He also promoted the arts and literature, and was a patron of the famous poet Malik Muhammad Jayasi.
After the death of Sikandar Lodi, his son Ibrahim Lodi ascended to the throne. Ibrahim Lodi was an ambitious ruler who sought to expand his empire through military conquests. He waged several wars against neighboring kingdoms, including those of Jaunpur, Bengal, and Gujarat. However, his aggressive policies soon brought him into conflict with the rising power of the Mughal Empire.
In 1526, Ibrahim Lodi faced off against the Mughal Emperor Babur in the Battle of Panipat. The battle was a decisive victory for Babur, and marked the end of the Lodhi Dynasty and the beginning of the Mughal Empire in India.
Despite its relatively short span of rule, the Lodhi Dynasty made several significant contributions to Indian history and culture. The rulers of the dynasty were known for their patronage of the arts, literature, and architecture. Several famous monuments, including the Lodhi Gardens in Delhi, the Bara Gumbad, and the Shish Gumbad, were built during their reign.
The Lodhi Dynasty was also known for its military prowess. The army of the Lodhis was composed of infantry, cavalry, and elephants, and was one of the most powerful forces in the region. The Lodhi rulers were also skilled administrators who implemented several important reforms, including the establishment of a standardized system of weights and measures, and the introduction of a system of land surveying.
Despite these achievements, the Lodhi Dynasty was ultimately unable to withstand the rise of the Mughal Empire. The Mughals, under the leadership of Babur, were able to conquer and establish their rule over most of the Indian subcontinent. Nevertheless, the legacy of the Lodhi Dynasty lives on, and their contributions to Indian history and culture continue to be celebrated to this day.